What is refrigerant?
It is a fluid circulating to transport energy inside air conditioners, refrigerators, and heat pump hot water heaters. It is a very important substance which hits blood if it says in man.
As a refrigerant, fluorocarbons (carbon and fluorine compounds) are used mainly, and it is generally referred to as fluorocarbons. Fluorocarbons were developed for refrigerators in the 1920s, and at that time they were touted as the chemicals of dreams. CFC (chlorofluorocarbon) and HCFC (hydrochlorofluorocarbon) are ozone depleting substances among fluorocarbons. These substances are called specific fluorocarbons. Since HFC (hydrofluorocarbon) does not have chlorine, it does not destroy the ozone layer, so its conversion has progressed as an alternative to specific fluorocarbons. For this reason, HFC is generally referred to as “alternative fluorocarbon”. However, it is found that alternative fluorocarbons have a greenhouse effect of several hundred times to tens of thousands of times as much as carbon dioxide, which is a problem as a cause of global warming. For this reason, further substitution sought, and even the reduction is required by the Kigali revision described in the future.
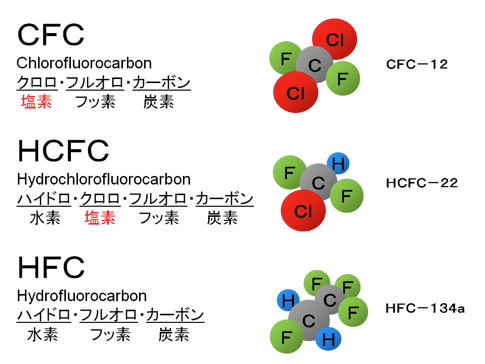
Types of refrigerant
In the table below, cfc, HCFC, and HFC-based fluorocarbons, typical refrigerants, are shown. There are various types of fluorocarbons in this series, and each refrigerant has a refrigerant number. Looking at this table, we can see that the coefficient of ozone depletion (ODP) is 0, but the global warming coefficient (GWP: relative value when CO2 is 1) is still a large number.
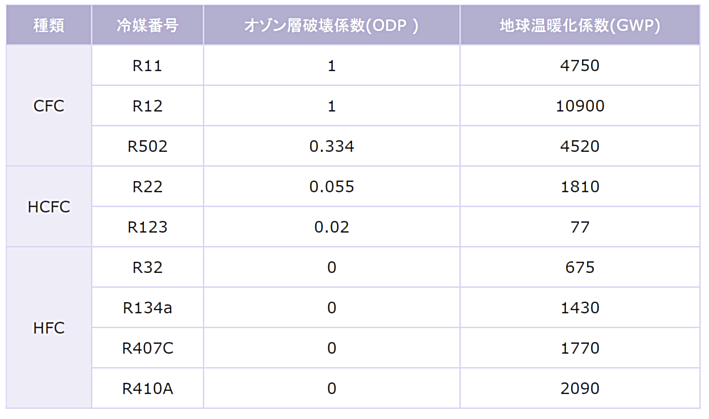
*Quotes from Figaro Giken Co., Ltd. website
For this reason, further refrigerant conversion is required, and now, attention is paid to HFO (hydrofluoroolefin) and natural refrigerant. Since many of these refrigerants have microburns, measures are urgently needed. The refrigerant has a long and short.
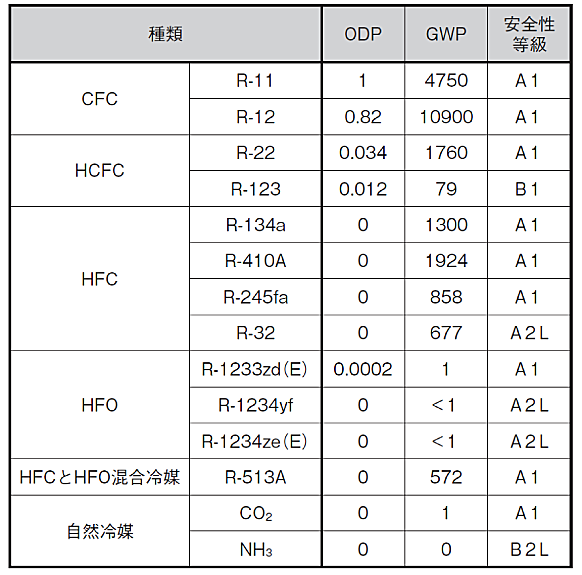
*Trends in refrigerants for air conditioning NTTf Research Institute
Principle of operation of equipment
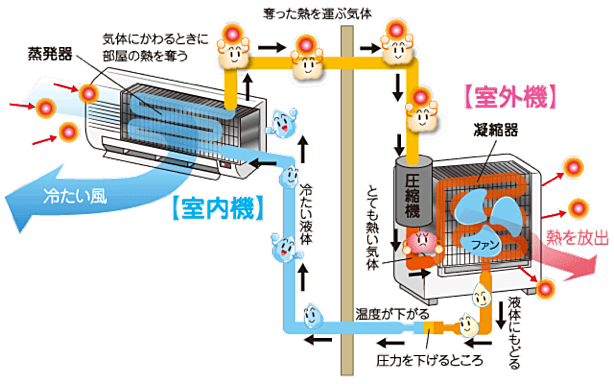
Air conditioners, refrigerators, and heat pump water heaters are all driven with the same operating principle. Figure 1 shows the state that the air conditioner is doing the air conditioning as an example. First of all, the operating principle is explained based on this operation state. The evaporator as a heat exchanger, the condenser, the compressor as a rotary machine driven by external power, and the expansion valve are the basic components. The interior unit has a built-in evaporator, and the outdoor unit has a condenser, compressor, and expansion valve. These components are connected by a pipe and the refrigerant flows and forms a heat pump cycle (also known as a refrigeration cycle). The refrigerant evaporates at about 5° even at a pressure state higher than atmospheric pressure, and it becomes the one that it wants to liquefy even about 30°.
Refrigerant vapor (1) at low temperature and low pressure flows into the compressor and is pressurized here, resulting in high temperature and high pressure. The power required to drive this compressor is the driving source of the air conditioner.
High-temperature and high-pressure refrigerants that flow out of the compressor flow into the condenser. In condensers, high-temperature-side fluids (outside air) have lower temperatures than refrigerant, so heat is transmitted from the refrigerant to the high-temperature side fluid, the refrigerant is cooled, and the refrigerant gas is condensed (liquefied). High-temperature side fluids are heated with heat.
The high-temperature and high-pressure condensate (3) that drains the condenser passes through the expansion valve. The expansion valve is a small hole, and when it passes through here, the refrigerant becomes low temperature and low pressure. This is just like being cooled when the fluid is released from a high pressure inner can to the low outside.
This low-temperature low-pressure refrigerant (4) flows into the evaporator. In the evaporator, heat moves from the low-temperature side fluid to the refrigerant by performing heat exchange with the low-temperature side fluid (in this case, indoor air) where the refrigerant of this low temperature and low pressure is higher than the temperature.
As a result, the refrigerant is heated, evaporated, and cools the low-temperature side fluid by the latent heat to obtain heat. The cycle is established by repeating this. During heating, by switching the internal flow direction, the heat exchanger of the outdoor unit plays the role of the condenser in the evaporator and the heat exchanger installed in the indoor unit. As a result, the high temperature air which got heat in the indoor unit circulates in the room. In the heat pump water heater, the hot water is taken out by the heat of water.
www.athome.tsuruga.fukui.jp
Ozone depletion problem
The ozone layer is a dense layer of ozone (O3) in the upper layer of the atmosphere. It absorbs harmful ultraviolet rays contained in sunlight and plays a role in protecting the life of the earth.
In the 1970s and 80s, it was discovered that the ozone layer over Antarctica was destroyed and a hole (ozone hole) was created. When destruction progresses, strong ultraviolet rays reach the surface of the earth without being absorbed by the ozone layer, causing skin cancer and adversely affecting the ecosystem.
So why has the ozone layer been destroyed? In fact, it was pointed out that the cause was cfc-based refrigerant, which is one kind of refrigerant used in many applications, such as air conditioners, refrigerator refrigerants, spray propellants, and printed circuit boards. Ozone depletion was caused by chlorine contained in CFC refrigerant seboteuring ozone.
It was because of this ozone layer destruction that the refrigerant became a big social problem originally. Since then, CFC refrigerant has been replaced by HFC refrigerant as an alternative refrigerant.
However, it was found that the HFC-based refrigerant was a global warming substance, and it was found that there was a greenhouse effect of thousands of times the carbon dioxide. Therefore, the problem of the refrigerant is a global warming problem now.
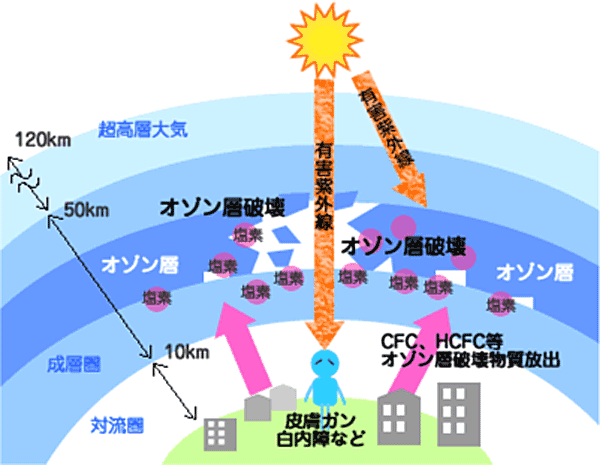
From Hyogo Prefecture Freon Recovery and Processing Promotion Council Website
Global Warming
Global warming has become a serious problem. The temperature of the earth is surely rising by the warming material including carbon dioxide. It has risen 0.74° in 100 years from 1906 to 2005. This causes the ice to melt in the North and South Poles and raise the surface of the sea. It is said that tuvalu, one of the lowest sea level countries in the world, is facing even the crisis of national annihilation.
Various natural disasters have been brought about. Floods, droughts, extreme heat and hurricanes. Of course, the scale increases large and a lot of lives are taken though it was originally.
In order to prevent such global warming, it is said that it is necessary to reduce the emissions of global warming substances by 50 from the present in order to reduce the temperature rise of the earth to less than 2°C by 2050.
Carbon dioxide is the most representative of global warming materials. However, fluorocarbons are said to have a global warming effect (GWP) thousands of times. Therefore, the reduction is hurried. By 2036, the HFC system, which is currently used mainly among fluorocarbons, must be reduced by 85 in developed countries.
This is the background behind the launch of w-refrigerant.com, a site that transmits information about refrigerants, and has come to share the exact information.
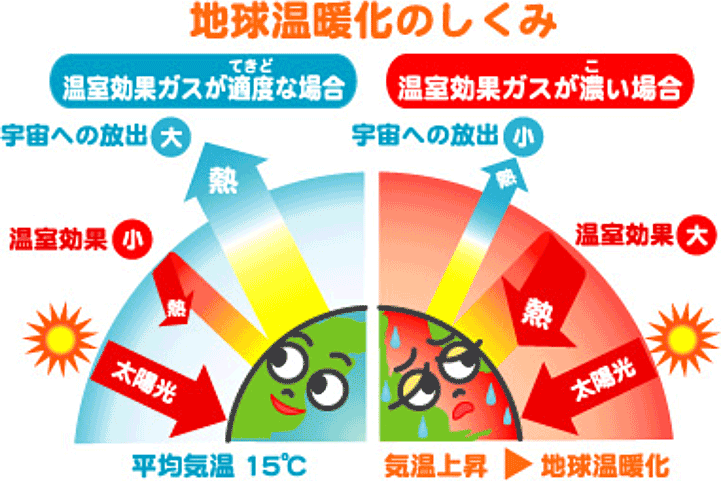
From asahi beverage website