NPO法人環境エネルギーネットワーク21主任研究員 石橋直彦
本稿では、米国における自動車用空調システムの整備・修理・廃棄のシステムの概要を紹介する。日本では使用済み自動車のリサイクル及び処理は自動車リサイクル法により規制されており、フロン、エアバッグ及びASR(自動車シュレッダーダスト)※1の3種類が処理対象物である。
以下にEPA(米国環境保護庁)のサイトに掲載された原文とその翻訳文を示す。
大気浄化法のもとでの自動車空調機器の修理に対するEPAの規制上の要件
自動車用空調システム(以下、カーエアコンと呼ぶ)は、冷凍サイクルを用いて車室を冷房する。本ページではこれらシステムの修理に対するEPAの規制と、これらの規制がサービス技術者、販売店経営者及び一部の冷媒小売業者に与える影響をについて説明する。規制のほとんどは大気浄化法第609条の規制に由来するが、米国大気浄化法の第608条と第612条も小さめの役割を果たす。EPAの規制要件の基本事項を以下に詳述する。
- 冷媒:EPAが承認したものでなければならず、意図的に環境に(大気中に)放出してはならない。
- 整備:いかなる種類であっても支払い(金銭以外の支払いを含む)が伴う場合、カーエアコンシステムで作業する全ての作業員は大気浄化法第609条に基づく認定を受け、承認された冷媒取扱設備を使用する必要がある。
- 冷媒の再利用:冷媒は、たとえ元の車両に戻す場合でも、再利用する前に適切にリサイクル又は再生する必要がある。
技術者研修及び認定
対価(例:報酬又は物々交換)を得てカーエアコンシステムの修理又は整備を行う技術者は、EPA認定の技術者研修・認定プログラムにおいて、大気浄化法第609条に基づく研修と認定を受けなければならない。システムで使用されている冷媒の種類に関わらず、カーエアコンシステムの修理又は整備を行うには、第609条の認定が必要である。
整備機材
技術者は、EPA又はEPAが承認した独立試験機関により認証された冷媒取扱機器を使用しなければならない。
冷媒取扱
カーエアコンシステムの整備や修理、又は冷媒が放出されることが当然予想されるその他の作業を行う前に、認証済みのサービス機器を使用して冷媒を回収しなければならない。回収した冷媒は、たとえそれが回収元のシステムに戻すものであっても、カーエアコンシステムへ再充塡する前に、再生又は再精製されなければならない。
回収した冷媒は、承認済みの冷媒回収再生充塡装置を使用して現場で再生するか、又は現場外の再精製施設に送付し、空調・暖房・冷凍協会(AHRI)規格700に従って精製することができる。再生(リサイクル)とは、不純物やオイルを除去する工程であり、再精製(リクレーム)は冷媒を新品同等の特性まで戻す工程である。冷媒を現場外に送付する場合は、EPA認定の冷媒再精製業者に送らなければならない。
放出禁止
大気浄化法第608条は、カーエアコンシステムを含む空調機器又は冷凍機器の保守、整備、修理、又は廃棄に際して、意図的に冷媒を放出することを禁止している。
“重大な新規代替物政策(SNAP)”により承認された代替冷媒のうち、唯一、二酸化炭素のみが第608条に基づく放出禁止の適用を免除されている。ただし、CO₂は第608条において大気中への放出が認められているものの、第609条の要件については免除されない。
整備事業者における記録保持要件
新参の整備事業者、又は初めてカーエアコンシステムを整備する事業者は、承認済みの冷媒取扱機器を取得し、適切に使用していることを担当のEPA地方事務所に証明する必要があるが、これは一度だけでよい。過去にクロロフルオロカーボンCFC 12 又はハイドロフルオロカーボンHFC 134a対応の冷媒取扱機器について所有を証明した事業者は、新しい機器を購入した場合でも、EPAに再度証明を提出する必要はない。これは、ハイドロフルオロオレフィンHFO 1234yf のような別種の冷媒用機器を購入する場合にも適用される。
機器を認証するには、当該機器を取得した者(事業所の所有者又は他の責任者)が署名した書面を提出する必要がある。この認証文書には以下を記さなければならない。
- 機器購入者の氏名
- 当該機器が設置される事業所の名称、住所、電話番号
- 当該事業所で使用するために取得した機器のメーカー名、型式番号、製造年及び製造番号
- 当該回収、回収・再生、又は回収・再生・再充塡機器が大気浄化法第609条に基づき承認されていること、機器の使用を許可された者全員が適切に訓練・認定を受けていること、ならびに提供する情報が真実かつ正確であることの表明
署名済みの認証文書は、当該事業所が所在する州を管轄するEPA地方事務所に送付する必要がある。各地方事務所の住所は別途参照可能である。
整備事業者は、整備機器を使用する全ての者が大気浄化法第609条に基づき適切に訓練・認定を受けていることを証明する記録を事業所内に保持しなければならない。さらに、回収した冷媒を送付した施設の名称及び住所に関する記録も事業所内に保持する必要がある。これらの記録は3年間保存しなければならない。
オゾン層破壊冷媒:販売制限及び記録保持要件
オゾン層破壊物質であるCFC又はHCFCを含む冷媒の販売又は流通は、大気浄化法第608条又は第609条に基づき認定を受けた技術者に制限される。20ポンド未満の容器に充塡されたCFC 12は、第609条認定技術者にのみ販売することができる。20ポンド未満の容器入りCFC 12を販売又は流通させる者は、購入者がEPA承認の第609条技術者訓練・認定プログラムによる認定を受けていることを確認しなければならない。
この要件の例外は、小型容器が再販のみを目的で購入される場合である。この場合、販売者は購入者から「転売目的である」旨を記した書面を取得しなければならない。当該書面には、購入者の氏名及び事業所住所を記載する必要がある。これらの記録は3年間保持しなければならない。いずれの場合も、販売者は販売場所において購入者に対する認定要件を明示した掲示を行う必要がある。
EPAは最近、“Cool Penguin F-12”として販売された製品の販売事例を確認した。この製品はオンライン販売を通じて自動車用空調向けに小型缶で流通しており、その内容はCFC 12、CFC 114、HCFC 142b及びHCFC 22と、そのほかに非オゾン層破壊物質を含む混合物であった。現在の規制では、これらの缶の輸入は違法であり、また、オゾン層破壊物質が規制日以降に無許可で輸入されたことを知っている場合、それらの販売や流通も禁止されている。オゾン層破壊物質の段階的廃止に関する詳細は Phaseout of Ozone-Depleting Substances (ODS) ※2を参照すること。
安全な廃棄に関する要件
カーエアコンシステムが廃棄段階に入った場合、廃棄処理過程の最終責任者は、冷媒を回収するか、又は機器を廃棄する前に、顧客が冷媒を回収済みあることを確認しなければならない。詳細は Stationary Refrigeration Safe Disposal Requirements※3を参照すること。
SNAP承認冷媒のうち、唯一二酸化炭素のみが第608条に基づく放出禁止の適用を免除されている。ただし、第608条においてCO₂の大気放出は認められているものの、第609条の要件は免除されない。
代替物質に関する政策(SNAP)プログラム
EPAは、大気浄化法第612条に基づき設立されたSNAPプログラムにおいて、代替冷媒を評価している。SNAPでは、カーエアコンシステム用冷媒を「条件付きで使用可能(acceptable subject to use conditions)」又は「不適格(unacceptable)」として分類する。個別のカーエアコン用冷媒に関する詳細や、CFC 12からHFC 134a、さらに低GWP冷媒(例:HFO 1234yf)への移行に関する情報はMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning Refrigerant Transition & Environmental Impacts※4を参照すること。
カーエアコンシステムに関連するSNAP規制要件
専用継手(Unique Fittings)
各SNAP承認冷媒は、異なる冷媒が誤って混合されるのを防ぐため、専用の継手を使用することが義務付けられている。これらの継手は、自動車本体、全ての回収・再生機器、缶用タップその他の充塡機器、及び全ての冷媒容器に取り付けられる。変換用アダプターを使用して継手を変更することは認められていない。
専用継手は、車両冷媒の純度を維持することで消費者を保護する。カーエアコンシステム用冷媒の専用継手サイズ及びラベル色に関する一覧は MVAC Refrigerants Fitting Sizes and Label Colors※5を参照すること。
マニホールドゲージ及び冷媒識別装置への適用
マニホールドゲージ又は冷媒識別装置に接続されるホース端部には標準化された継手を使用できるが、カーエアコン用システム及び整備機材に接続されるホース端部には、専用継手を恒久的に取り付けなければならない。
一種類の冷媒用アダプターを取り付け、その後取り外して別の冷媒用継手に交換することは認められない。基本原則として、一度ホースに取り付けられた継手は恒久的なものであり、取り外すことはできないとされる。
米国イノベーション・製造法(AIM法)第(i)項に基づくEPA技術移行プログラム
技術移行プログラム
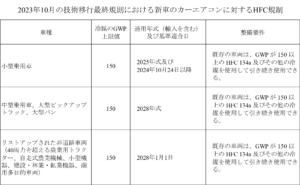
2023年10月24日、EPAは“ハイドロフルオロカーボンの段階的削減:米国イノベーション・製造法(AIM法)2020に基づく特定HFCの使用制限”に関する最終規則を公布した。本規則は、エアゾール、発泡体、冷凍・空調・ヒートポンプ(RACHP)製品及び機器において、高GWPのHFC使用を制限することにより、分野・部門ごとの冷媒の移行を実施するものである。当該規則では、GWP150以上のHFC(例:HFC 134a)の使用が、新たに製造又は輸入される小型乗用車、中型乗用車、大型ピックアップトラック、完成車両としての大型バン、及び特定のオフロード車両において制限される。詳細は 2023 Technology Transitions Final Rule※6を参照すること。なお、本最終規則は既存のMVACシステムの整備・修理におけるHFC冷媒の使用を制限するものではない。そのため、既存のMVACシステムを整備、修理、又は改修する技術者は、引き続きHFCを使用することが可能である。
注:
※1 自動車シュレッダーダストとは、使用済み自動車を破砕・解体した後、鉄などの有用金属を回収した残りの部分で、主にプラスチック、ガラス、ゴム、繊維などの混合物のこと
※2 https://www.epa.gov/ods-phaseout
※3 https://www.epa.gov/section608/stationary-refrigeration-safe-disposal-requirements
※4 https://www.epa.gov/mvac/acceptable-refrigerants-and-their-impacts
※5 https://www.epa.gov/mvac/unique-fittings-label-colors-mvac-refrigerants
【以下原文】
Regulatory Requirements for MVAC System Servicing
EPA Regulatory Requirements for MVAC Servicing under the Clean Air Act
Motor vehicle air conditioning (MVAC) equipment uses refrigeration to cool the driver's or passenger's compartment. This page describes EPA requirements for servicing these systems, and how these requirements impact service technicians, shop owners, and some refrigerant retailers. Most of these requirements come from regulations under section 609 of the Clean Air Act (CAA), while two additional sections of the CAA, 608 and 612, play smaller roles.
Here are the basics on EPA’s regulatory requirements, explained in more detail below:
- Refrigerant: Must be approved by EPA and cannot be intentionally released (vented) to the environment.*
- Servicing:When payment of any kind is involved (including non-monetary), any person working on an MVAC system must be certified under section 609 of the CAA and they must use approved refrigerant handling equipment.
- Reusing Refrigerant:Refrigerant must be properly recycled or reclaimed before it can be reused, even if it is being returned to the vehicle from which it was removed.
Technician Training and Certification
Technicians who repair or service MVAC systems for consideration (e.g., payment or bartering) must be trained and certified under CAA section 609 by an EPA-approved technician training and certification programs. Section 609 certification is required to service any MVAC system for consideration, regardless of what refrigerant is used in the system.
Servicing Equipment
Technicians must use refrigerant handling equipment that has been certified by EPA or an independent standards testing organization approved by EPA to certify equipment.
Refrigerant Handling
Certified servicing equipment must be used to remove refrigerant prior to servicing or repairing an MVAC system or conducting any other service on a vehicle during which discharge of refrigerant can reasonably be expected. Recovered refrigerant must be either recycled or reclaimed before it can be recharged into an MVAC system, even if the refrigerant is being returned to the system from which it was removed.
Recovered refrigerant can either be recycled on-site using approved equipment designed to both recover and recycle refrigerant or sent off-site to a reclamation facility to be purified according to Air-Conditioning, Heating and Refrigeration Institute (AHRI) Standard 700. Recycling removes impurities and oil, while reclamation returns the refrigerant to virgin specifications. Refrigerant sent off-site must be sent to an EPA-certified refrigerant reclaimer.
Venting Prohibition
Section 608 of the Clean Air Act prohibits the intentional release (venting) of any refrigerant when maintaining, servicing, repairing, or disposing of air conditioning or refrigeration equipment, including MVAC systems.
*Of the Significant New Alternatives Policy (SNAP)-approved alternatives only one refrigerant, carbon dioxide (also known as R 744 or CO2), is exempt from the venting prohibition under section 608. Although CO2 can be released to the environment under section 608, it is not exempt from the section 609 requirements.
Recordkeeping Requirements for Service Shops
New service shops or shops servicing MVAC systems for the first time must certify to their EPA Regional Office that they have acquired and are properly using approved refrigerant handling equipment. This is a one-time requirement. If a shop has certified ownership of a piece of chlorofluorocarbon CFC-12 or hydrofluorocarbon HFC-134a equipment at any time in the past, the shop is not required to re-submit certification to EPA when they purchase new equipment. This applies even if the shop purchases equipment for a different refrigerant, such as hydrofluoroolefin HFO-1234yf.
To certify your equipment, provide a written statement signed by the person who acquired the equipment (this person may be the owner of the establishment or another responsible officer). This certification statement shall include:
- The name of the purchaser of the equipment;
- The name, address, and telephone number of the establishment where the equipment is located;
- The name brand, model number, year and serial number(s) of the equipment acquired for use at the above establishment; and
- A statement that your recover, recover/recycle, or recover/recycle/recharge equipment is approved under Section 609 of the Clean Air Act, that each individual authorized to use the equipment is properly trained and certified, and that the information provided is true and correct.
Send your signed certification statement to the EPA Regional Office responsible for the state in which the establishment is located. Addresses for each regional office can be found here.
Service shops must maintain on-site records proving that each person using servicing equipment has been properly trained and certified under Section 609. Additionally, they must maintain records on-site of the name and address of any facility to which they send recovered refrigerant. Records must be maintained for 3 years.
Ozone-Depleting Refrigerants: Sales Restrictions & Recordkeeping Requirements
The sale or distribution of any refrigerant containing ozone-depleting CFCs or HCFCs is restricted to technicians certified under section 608 or section 609 of the CAA. CFC-12 in a container of less than 20 pounds may only be sold to technicians certified under section 609. Any person who sells or distributes CFC-12 in containers less than 20 pounds must verify that the purchaser has obtained certification by an EPA-approved section 609 technician training and certification program.
An exception to these requirements is when small containers are purchased for resale only. In this case, the seller must obtain a written statement from the purchaser that the containers are for resale only. The statement must include the purchasers name and business address. Records must be maintained for 3 years.
In all cases, the seller must display a sign where sales occur stating the certification requirements for purchasers.
The U.S. EPA recently identified sales of a product marketed as Cool Penguin “F-12.” Sold in small cans through online retail platforms for motor vehicle air conditioner use, the mixture consisted of CFC-12, CFC-114, HCFC-142b and HCFC-22, along with non-ozone depleting components. Under current regulations, not only is the import of these cans illegal, no person may sell or distribute, or offer for sale or distribution, any regulated ozone-depleting substance that they know, or have reason to know, was imported illegally (e.g., without appropriate allowances or after the phaseout date for that chemical). For more information on the phaseout of ODS, please visit EPA ODS Phaseout.
Safe Disposal Requirements
When an MVAC system enters the waste stream, the final person in the disposal chain must remove the refrigerant, or make certain that their customer has removed it, prior to disposal. For additional information see safe disposal requirements.
*Of the SNAP-approved alternatives only one refrigerant, carbon dioxide (also known as R-744 or CO2), is exempt from the venting prohibition under section 608. Although CO2 can be released to the environment under section 608, it is not exempt from section 609 requirements.
Significant New Alternatives Policy (SNAP) Program
EPA evaluates alternative refrigerants under its SNAP program, established under section 612 of the CAA. SNAP lists refrigerants for MVAC systems as either “acceptable subject to use conditions” or “unacceptable.” For additional information on the individual MVAC refrigerants, and the transition from CFC-12 to HFC-134a to lower-GWP refrigerants (e.g., HFO-1234yf), see the webpage "Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning Refrigerant Transition & Environmental Impacts."
SNAP regulatory requirements related to MVAC systems is explained below:
Unique Fittings
Each SNAP-approved refrigerant is required to be used with a unique set of fittings to prevent the accidental mixing of different refrigerants. These fittings are attachment points on the car itself, on all recovery and recycling equipment, on can taps and other charging equipment, and on all refrigerant containers. An adapter should not be used to convert a fitting.
Unique fittings help protect the consumer by helping to protect the purity of refrigerant in their vehicle. For a list of the MVAC refrigerant unique fittings see "MVAC Refrigerants Fitting Sizes and Label Colors."
Applicability of Unique Fittings to Manifold Gauges and Refrigerant Identifiers
A standardized fitting may be used at the end of hoses attached to manifold gauges or a refrigerant identifier, but unique fittings must be permanently attached at the ends of the hoses that attach to MVAC system and servicing equipment.
Adapters for one refrigerant may not be attached and then removed and replaced with the fitting for a different refrigerant. The guiding principle is that once attached to a hose, the fitting is permanent and cannot be removed.
EPA Technology Transitions Program under Subsection (i) of the American Innovation and Manufacturing (AIM) Act
Technology Transitions Program
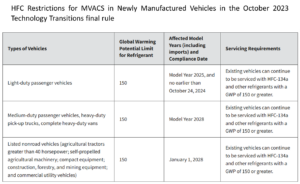
On October 24, 2023, EPA issued a final rule Phasedown of Hydrofluorocarbons: Restrictions on the Use of Certain Hydrofluorocarbons under the American Innovation and Manufacturing Act of 2020, to implement sector-based transitions through restrictions on higher-GWP HFCs in aerosol, foams, and RACHP (refrigeration, air conditioning, and heat pump) products and equipment. The rule restricts the use of HFCs with a GWP of 150 or greater (e.g., HFC-134a) in newly manufactured and imported light-duty vehicles, medium-duty passenger vehicles, heavy-duty pick-up trucks, complete heavy-duty vans, and certain nonroad vehicles. See the 2023 Technology Transitions Final Rule. This final rule does not restrict the use of HFC refrigerants in the servicing or repair of existing MVAC systems. So, technicians that service, repair, or retrofit existing MVAC systems can continue to use HFCs.
Last updated on December 20, 2024